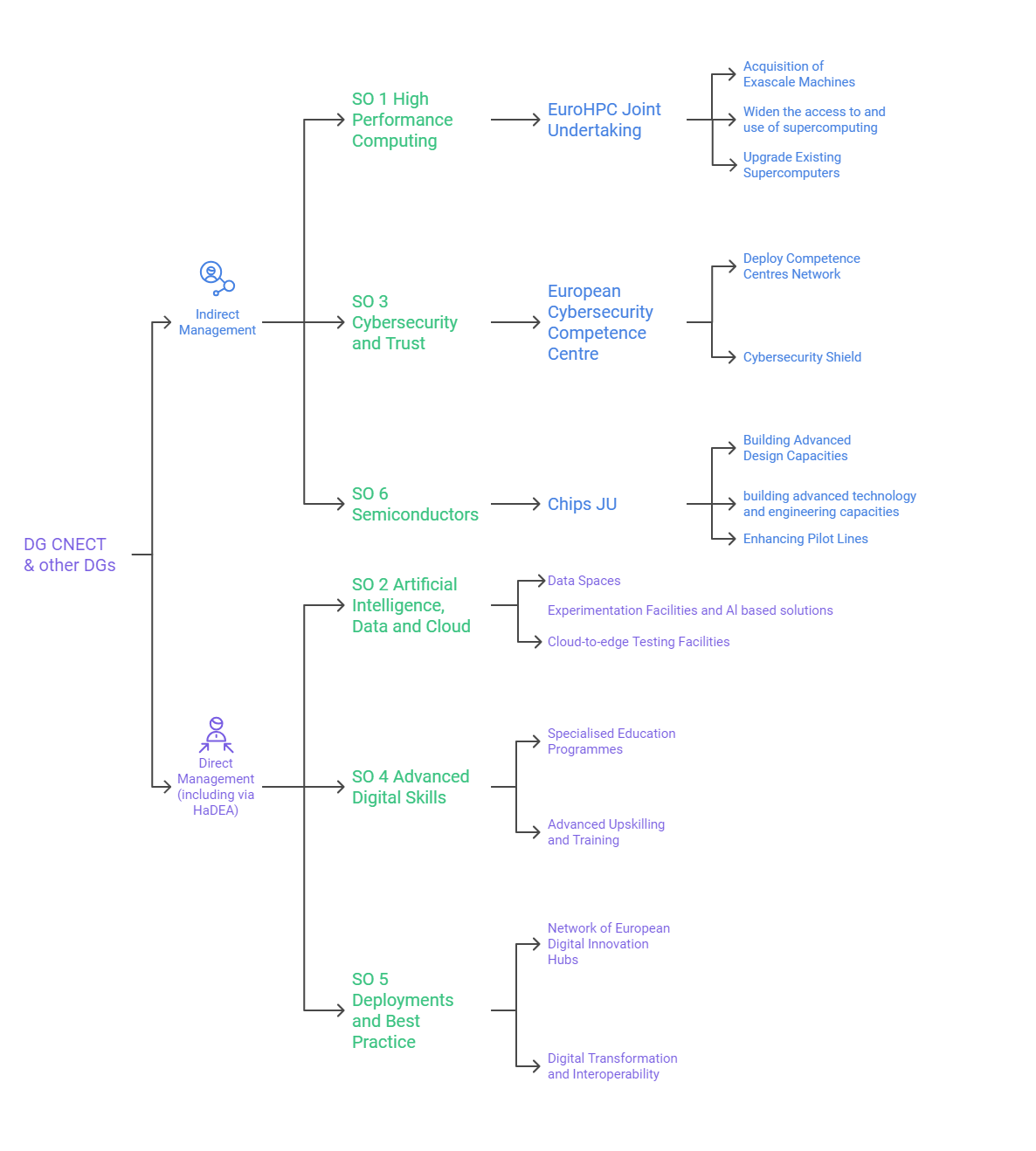
The DIGITAL Europe Programme (DIGITAL) is the EU initiative designed to strengthen Europe’s digital transformation by funding projects in six critical areas: supercomputing, artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, advanced digital skills, semiconductors and digital technologies. The implementation of DIGITAL relies on an intricate governance structure involving several bodies at both the EU and national levels. These include the European Commission's Directorate-Generals (DGs), executive agencies like HaDEA, joint undertakings such as EuroHPC and Chips JU, and specialised bodies like the European Cybersecurity Competence Centre (ECCC).
In addition to these implementing bodies, DEDEP.eu, a platform dedicated to dissemination & exploitation activities, acts as a bridge between the DIGITAL programme’s results and the broader community of potential beneficiaries. This include facilitating collaboration, offering tools and providing strategic guidance across the various DIGITAL funding mechanisms.
The European Commission and Its Directorate-Generals (DGs)
At the highest level, the European Commission oversees DEP’s strategic direction and financial management. The Directorate-General for Communications Networks, Content and Technology (DG CNECT) is the lead entity, responsible for setting objectives, allocating budgets, and monitoring implementation. Other DGs contribute based on their area of expertise. DG CNECT manages key objectives such as artificial intelligence, high-performance computing (HPC), cybersecurity, and digital skills. It also cooperates with implementing bodies such as HaDEA, EuroHPC-JU, and ECCC to ensure smooth execution. DG DIGIT focuses on interoperability, which is a critical aspect of the Digital Single Market, ensuring that national frameworks align with EU interoperability standards. DG GROW and DF FISMA oversee aspects related to public procurement data infrastructure and financial data spaces, crucial for digital transformation in the financial sector.
A specific example of the Commission's role is DG CNECT Unit C1 "Open Science and Digital Modelling" (CNECT.C1), which leads Destination Earth (DestinE), a key project aimed to build a high-precision digital twin of the Earth in the form of a platform that will provide data, models, predictions of the state of the Earth. This initiative is supported by entities such as the European Space Agency (ESA), the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), and EUMETSAT.
The Health and Digital Executive Agency (HaDEA)
The Health and Digital Executive Agency (HaDEA) is responsible for implementing parts of DIGITAL related to artificial intelligence, advanced digital skills, and digital infrastructure deployment. As an executive agency, HaDEA is in charge of the financial and budgetary aspect of the programme. Additionally, HaDEA oversees projects like the European Digital Media Observatory (EDMO) and the CIRPASS initiative, which supports digital "product passports", important components of the European Green Deal. Additionally, it manages grant agreements for data spaces, semiconductor skills development, and digital training programmes specifically for young women.
Joint Undertakings and Specialised Bodies
Several joint undertakings (JUs) and competence centres play a key role in DEP’s implementation through indirect management, focusing on specific technological domains. EuroHPC Joint Undertaking (EuroHPC-JU), for instance, manages high-performance computing (HPC) and quantum computing projects, with €1.9 billion from DIGITAL designated for exascale supercomputers, HPC infrastructure, and skills development. EuroHPC-JU also aligns efforts with Horizon Europe and the Connecting Europe Facility (CEF2) to ensure complementary actions.
Chips Joint Undertaking (Chips JU) oversees initiatives under DEP’s semiconductor objective, including the establishment of Competence Centres for Semiconductors and pilot lines for advanced semiconductor technologies. European Cybersecurity Competence Centre (ECCC), instead, is responsible for DEP’s cybersecurity-related actions, working with a Network of National Coordination Centres (NCCs) to strengthen Europe’s cybersecurity capabilities and industry.
Each of these entities manages its own work programme, defining call topics, budgets, and evaluation processes while maintaining alignment with DEP’s broader objectives.
Collaboration with other programmes
DIGITAL also plays an important role in complementing and reinforcing other major EU funding programmes, ensuring strategic investment in Europe’s digital future. For instance, Horizon Europe complements DEP’s emphasis on large-scale deployment, cybersecurity research, and AI experimentation, while Connecting Europe Facility (CEF2) invests in high-capacity broadband and 5G corridors, providing the infrastructure backbone for DEP’s digital services. European Regional Development Fund (ERDF), instead, co-funds initiatives such as the European Digital Innovation Hubs (EDIHs), which receive up to 50% of their funding from DEP, with the remainder coming from ERDF or other public/private sources. Last but not least, InvestEU supports investments in strategic digital technologies and skills through the Investment Platform for Strategic Digital Technologies, managed by the European Investment Fund (EIF).
Through these synergies, the programme maximises its impact while ensuring coherence across EU digital investment strategies.
The European Digital Innovation Hubs (EDIHs)
A fundamental actor of DEP’s implementation is the European Digital Innovation Hubs (EDIHs), which provide hands-on support for SMEs and mid-caps in their digital transformation journeys. EDIHs offer businesses with hands-on assistance, enabling them to explore and adopt new digital technologies with confidence. One of their key functions is to offer testing and experimentation services, allowing companies to trial solutions before committing to major investments. In addition, EDIHs focus on digital skills training and development, so that businesses and their employees are equipped with the expertise needed to thrive in this increasingly digital economy. Beyond technical support, they also help businesses secure investment, providing guidance on financing options to scale up their digital solutions effectively. However, their role extends beyond direct business support; EDIHs act as connectors within the broader digital ecosystem, linking companies with test and experimentation facilities, cybersecurity networks, and data spaces.
Conclusion
Within this complex landscape, DEDEP.eu provides invaluable support to DIGITAL beneficiaries. Operating as a strategic framework to amplify the impact of the EU projects, DEDEP.eu offers guidance, tools and support in order to bridge the gap between technological advancement and practical applications. This allows projects to navigate the various funding opportunities and strategies to make sure that DEP-funded initiatives contribute to a stronger, more competitive European digital sector.
